Four Questions that Guided the Evaluation
- What has been the nature, extent, and evolution of support to health services in the last 10 years?
- How relevant has World Bank Group support to health services been to the main health needs and priorities?
- To what extent has World Bank Group support effectively contributed to the achievement of its goals?
- What has been the role of the World Bank Group in global and country levels partnerships supporting health services?
Main Findings: Focusing on Client Needs
World Bank Group support to health services shows good alignment with the health needs and priorities of client countries. World Bank project financing shows a positive correlation with both the overall burden of disease and the relative importance of disease burden in the client countries.
The predominant health focus in World Bank projects’ interventions is consistent with countries’ epidemiological transitions and income level. The higher the level of gross domestic product per capita the more is the support to general health and noncommunicable diseases.
Alignment of IFC investments with health needs shows that IFC seems to be in where the needs are large, but also where the business environment is good enough for private sector companies to deliver services with positive returns, However, IFC is active in only about one-third of countries having high needs and good business environment, which suggests that there is potential for IFC investments to expand beyond countries in its current portfolio.
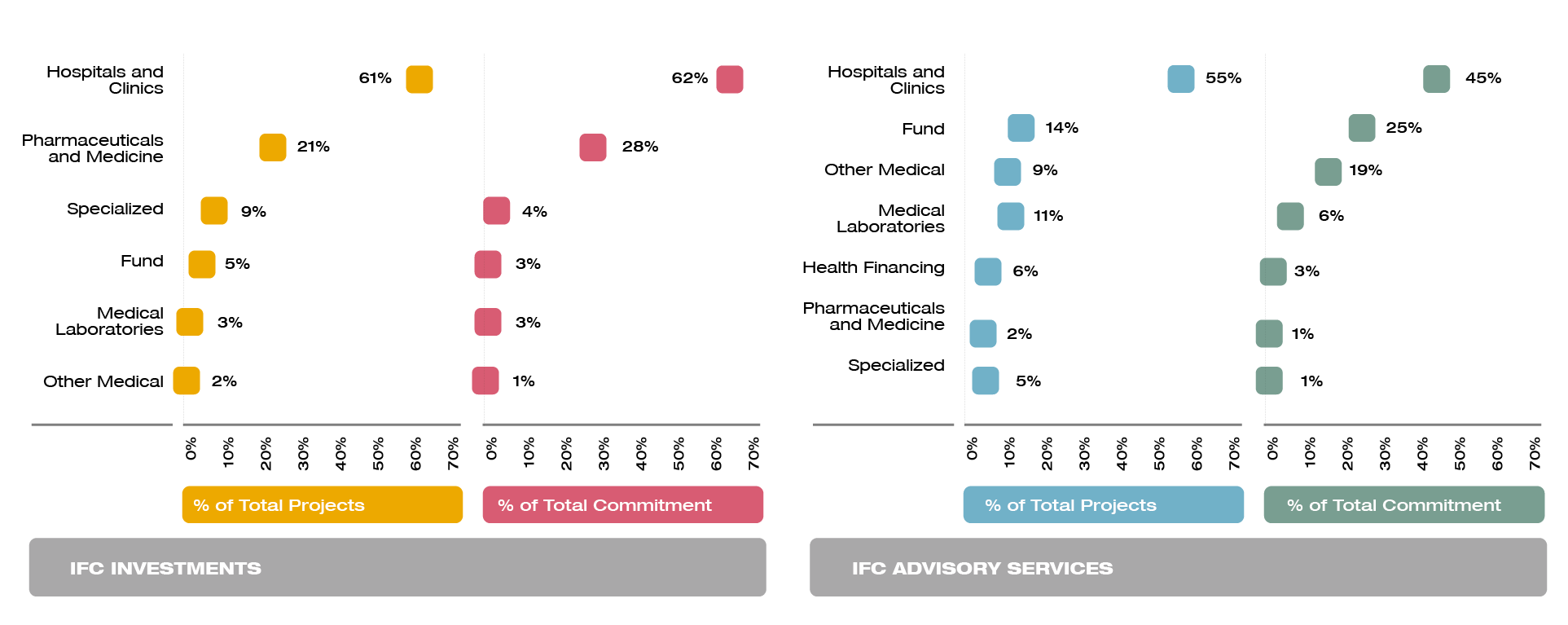
IFC’s Investment and Advisory Services projects largely reflect the health priorities of middle-income countries. IFC focuses more on noncommunicable diseases and general health. Most support goes to hospitals, clinics, and pharmaceutical companies with a high concentration in large markets. IFC advisory assistance is concentrated on Public-private partnerships accounting for about 69 percent of total projects.
Main Findings: Key Drivers of Universal Health Coverage
The World Bank Group is addressing key drivers of universal health coverage although with different levels of emphasis across the key drivers. The most frequent objectives sought by World Bank Group–financed projects are the improvement of access, quality, or health systems. Objectives related to health outcomes and equity are less frequently pursued.
Improve access. The World Bank has made substantial contributions to improving access to health services. It is an objective in 54 percent of World Bank–financed projects approved during the evaluation period, and it has been achieved in 70 percent of the 259 evaluated projects. IFC also contributed to improved access to health services. It is an objective in 88 percent of the investment projects, and it has been achieved in 73 percent of its evaluated projects. However, due to the limitation of the monitoring frameworks of IFC projects, it is not possible to determine if they contributed to expanding coverage or to improving availability and use among those who were already covered.
Improve quality. Quality improvement is an objective in 27 percent of World Bank-financed projects. Over time, World Bank–financed projects show, greater emphasis on improving the quality of health services (from 18 percent among closed to 44 percent among open projects) but only partial success. Only 46 percent of quality improvement objectives in evaluated projects have been rated positively (moderately satisfactory and above). IFC projects frequently included quality improvement objectives, but with a declining trend (from 27 percent among closed to 19 percent among open projects). Moreover, IFC quality improvement objectives and indicators focus on a narrow aspect of quality (structure).
Strengthen health systems. The second most common project objective, it is included in about 37 percent of World Bank–financed projects. However, the presence of this type of objective has been decreasing over time, even if health systems strengthening activities are identified in about 90 percent of projects. Additionally, about 55 percent of the health systems strengthening objectives have been rated positively.
Improve equity. Few World Bank–supported projects have objectives that explicitly aim at improving equity. However, there seems to be an implicit equity focus in many projects. In fact, the majority (64 percent) of World Bank–financed projects target specific disadvantaged population groups (often the poor). IFC also strives to invest in clients with a strong focus on corporate social responsibility. However, the distributional impact of World Bank and IFC projects is not known.
Improve health outcomes. Explicit objectives toward health improvement are present in 29 percent of World Bank–financed projects, but with a reduced frequency over time (from 35 percent among closed to 16 percent among open projects) and in only 1 percent of IFC projects. About half of the World Bank–financed projects reached the desired health improvement objectives.
Read more in Chapter 4: The Drivers of Universal Health Coverage
Main Findings: Performance-based Financing
World Bank project financing adopting Performance-based Financing (PBF) interventions performs better than the World Bank portfolio in improving access, quality, and health outcomes. The World Bank contributed to expanding the knowledge and use of incentives to encourage health providers to improve access to and quality of health services, mainly through the HRITF. The sustainability and scale-up of the pilots were successful in some instances but are still a challenge in many countries. Efforts should be directed at continuing to generate more evidence on PBF and at ensuring good practices are scaled up nationally.
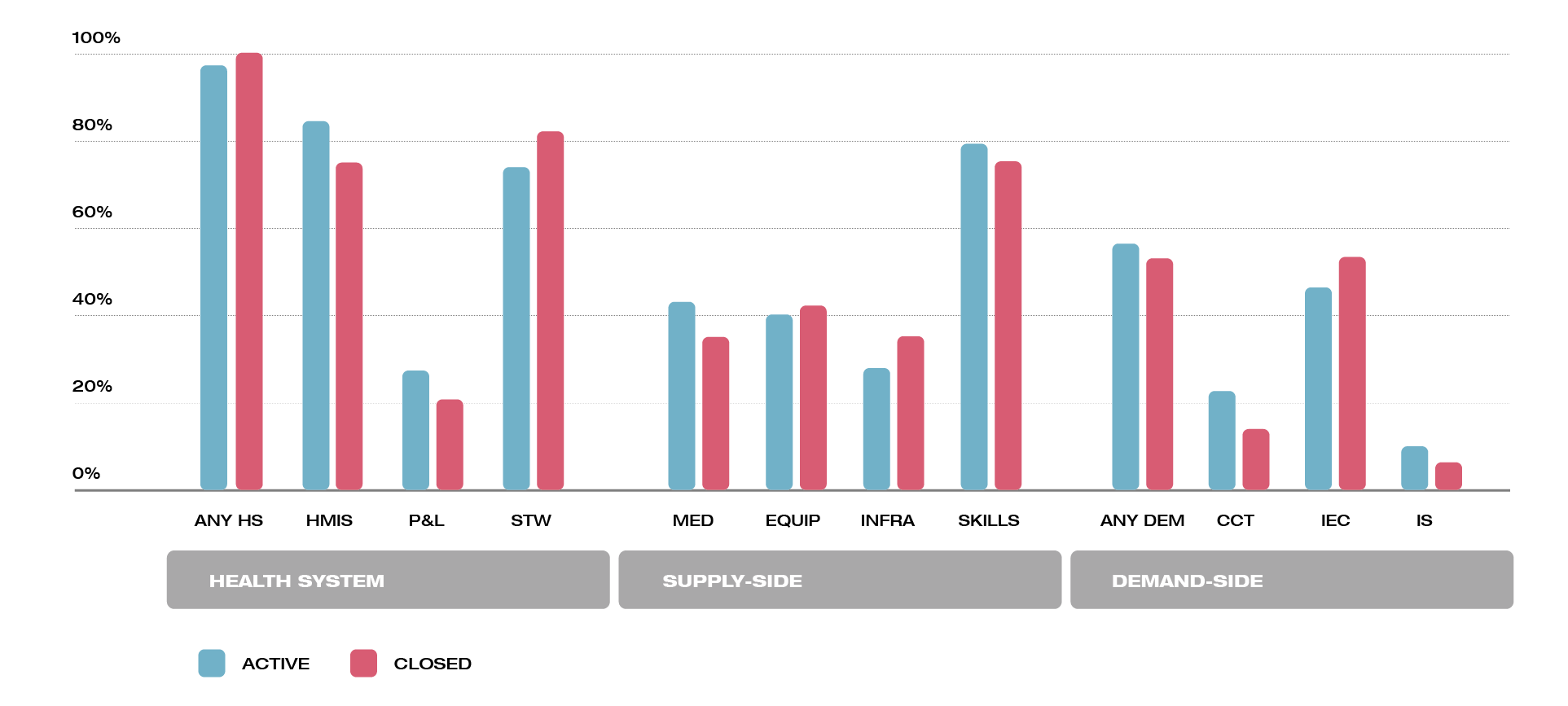
The design of World Bank–financed projects supporting Performance-based Financing (PBF) interventions had an integrated approach that combined supply, demand and system wide activities. Supply-side interventions addressed health workers’ motivation (“can-do” gap—difference between what health staff is capable of doing and what they do in practice); skills and knowledge (“know-how” gap—staff cannot do better than what they how to do); and system capacities (“know-can” gap—installed capacity limits health staff practice). They have also blended demand-side approaches to tackle access barriers and encourage use of health services. It appears to be a slight shift in investments from traditional IEC activities toward other more sophisticated approaches such as CCT. Almost all projects included activities addressing the entire health system consistent with the importance of a strong and reliable HMIS to monitor PBF programs, and for the MOH stewardship and regulation functions.
Read More about the Evolution and World Bank Group Strategies for Performance-based Financing
Main Findings: Public-Private Interactions
The World Bank’s support to articulate private service provision and public financing is still limited, and IFC investee companies face challenges in integrating with public financing. This specific aspect of strengthening health system functions was found in only 7 percent of World Bank–financed projects (46 of 619 projects approved during FY05–16). Most IFC investments (48 projects, or 53 percent of the portfolio) went to companies seeking both private and public financing for their health services. However, the IEG review found that hospitals and specialty chains supported by IFC investments did not manage to attract public financing (as expected) and continued to rely primarily on out-of-pocket payments. Internally, limited collaboration between the World Bank and IFC continues to be a bottleneck in the provision of integrated solutions.
The inadequate integration of IFC investments within public financing reduces their potential to expand coverage among the poor and their contribution to universal health coverage. The poor have little capacity to pay for health services, thus the integration of private provision with public financing is— usually—necessary to make health services affordable, and thus accessible to them (Hammer, Aiyar, and Samji 2007).
Read More about World Bank Group Support to Public-Private Interaction
Main Findings: Response to Pandemic Outbreaks
The World Bank Group’s performance in pandemic preparedness and control has improved with successive pandemic outbreaks. The World Bank supported 63 countries under the Global Program on Avian Influenza Control and Human Pandemic Preparedness during 2006–13. However, the World Bank failed to sustain this early effort. More recently, the World Bank was a vital member of the global coalition that fought the Ebola outbreak in West Africa in 2014–15. It quickly mobilized financial resources needed to stop the outbreak and helped restore basic health services in the three West African countries affected by the pandemic. The Pandemic Emergency Financing Facility, approved in May 2016, is expected to accelerate the release of funds to respond to future outbreaks.
A key lesson that has emerged from World Bank Group support in pandemic situations is that capable health systems are a necessary ingredient to mount a successful response to deadly virus outbreaks. They require adequately staffed health services, a supply of essential personal protective equipment, capacities for laboratory diagnosis, clinical management, and surveillance for quick diagnosis and rapid contact tracing.
Read More about World Bank Support for Pandemic Preparedness and Control
The World Bank Group and the Global Health Landscape
The urgency of reaching the SDGs and universal health coverage by 2030 requires all actors of the global aid architecture to join forces and share resources, expertise, and knowledge. The World Bank Group with its global reach and stature is well positioned to foster collaboration among global players.
The global health landscape has become more complex. This complexity arises primarily from the increase in the multiplicity of actors. The size and diversity of funding instruments adds to the intricacy. Development assistance for health has increased from $6 billion in 1990 to more than $37 billion in 2015.
The complexity of the global development landscape, the appearance of new actors, and the proliferation of partnerships globally require an improvement in the strategic focus of the World Bank Group’s participation in global partnership programs.
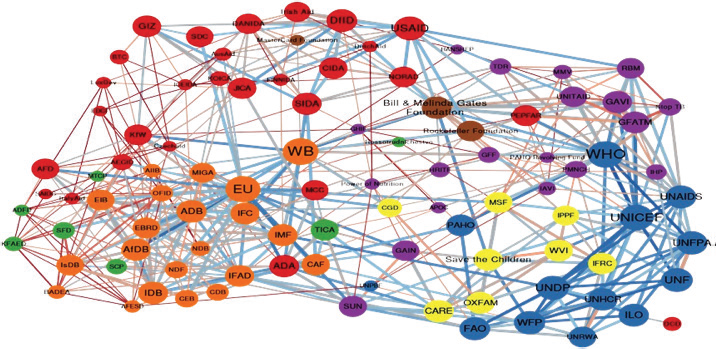
This evaluation found that the World Bank Group plays a central role in online interactions among global development actors, and it collaborates directly or through GPPs with almost all relevant actors. Using social network analysis to visualize how organizations operating in the global health landscape. The World Bank relates directly or through GPPs with almost all relevant actors, it has a central position in the network, and it is potentially able to spread information effectively through the online network of development actors.
Read More about the World Bank and the Global Health Landscape
Recommendations
Recommendation 1: Improve measurement of the quality of health services and the distributional effects of health services projects. The World Bank Group should continue improving the monitoring and evaluation framework of health services projects. In particular, the monitoring and evaluation framework should include (i) appropriate indicators of the relevant dimensions of health service quality – structure, process, and outcomes and (ii) the measurement of improvements of beneficiaries relative to nonbeneficiaries.
Recommendation 2: Strengthen World Bank and IFC synergy to support public-private interactions in client countries to contribute to SDG3 and universal health coverage. (i) For World Bank, work with the IFC to strengthen the planning, regulatory, and accountability arrangements for public-private interactions. (ii) For IFC, work with the World Bank to crowd-in public financing for privately delivered services. The World Bank Group’s newly launched Maximizing Finance for Development (MFD) approach, aimed at systematically mobilizing finance by focusing on upstream reforms and other constraints to private sector investment to address market failures, can be applied to achieve greater synergies between the public and private sector.
Recommendation 3: To develop sustainable capacity to address pandemics, systematically integrate, in World Bank Group–financed projects and advisory services in health services, awareness and preparedness plans and governance frameworks for pandemic control within the client country’s own health system. Building on the commitment made under IDA18 to support health emergency preparedness, response, and recovery, the management of the World Bank Group institutions could seek to ensure that World Bank’s project financing and ASA are not one-off responses outside the client country’s health system.
Recommendation 4: Enhance the strategic alignment and selectivity of World Bank Group engagement in ongoing and future global partnership programs. A strategic review should apply clear selectivity criteria that reflect the World Bank Group’s comparative advantage and the broader global development agenda. It can inform the selectivity and relevance of ongoing and future GPPs, and a more effective use of resources needed for engaging in partnerships.