The Operating Model and How it Changed
Reforms to the World Bank’s operating model sought to:
- improve global knowledge flow and technical collaboration to deliver more integrated, multisector solutions to clients.
- focus country programs more selectively on tackling critical issues.
- better deliver on global priorities.
- deepen the World Bank’s ability to deliver expertise grounded in thought leadership and global knowledge curation.
- Reforms resulted in unanticipated managerial challenges and the model has remained in flux. Dispersing the central change management team and undertaking simultaneous budget cuts caused lack of continuity in reform implementation. Some proposed measures on incentives and leadership never materialized.
Read more about the World Bank’s Operating Model and how it changed in Chapter 2.
View the structure of the World Bank operational complex as a result of the reforms to the operating model
See Glossary of Terms for more information about each staff position and technical groups
Findings on Knowledge Flow
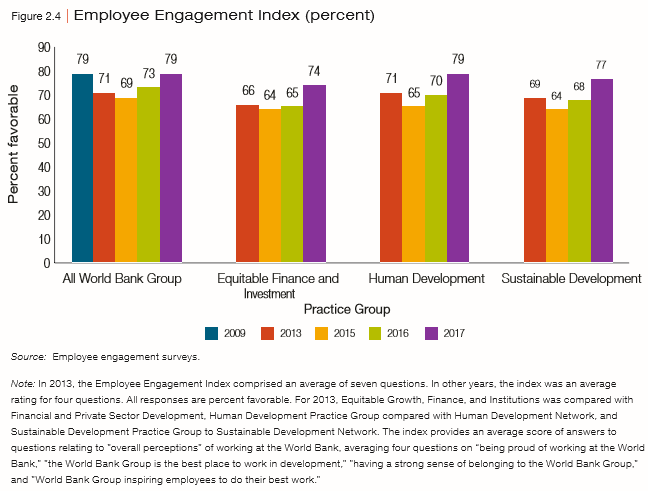
- Larger country programs tend to attract global knowledge more easily than smaller ones.
- Staff is increasingly positive about knowledge flows. This is according to staff responses to the annual engagement survey and interviews. GP staff believe knowledge flow has improved and collaboration inside GPs is easier because of enhanced staff mobility.
- Staff also perceive client services have improved at least some of the time.
- Some GPs have coherent and systematic approaches to managing and investing in knowledge, others less so. This often reflects the availability of trust funds and leadership support.
- Contestability in quality assurance is uneven.
- Global Solutions Groups (GSGs) have performed unevenly, with few consistent mechanisms to channel knowledge into country programs. Although views on Global Leads (GLs) vary, GLs often suffer from unclear roles and unfunded mandates and the role has been recast or disbanded in some GPs.
- The Global Themes (GTs) support coherent approaches to the World Bank’s cross-cutting priorities, making them a valuable addition to the operating model
Read more in Chapter 3: Global Knowledge Flow
View the structure of the World Bank operational complex as a result of the reforms to the operating model
See Glossary of Terms for more information about each staff position and technical groups
Findings on Collaboration for Integrated Solutions
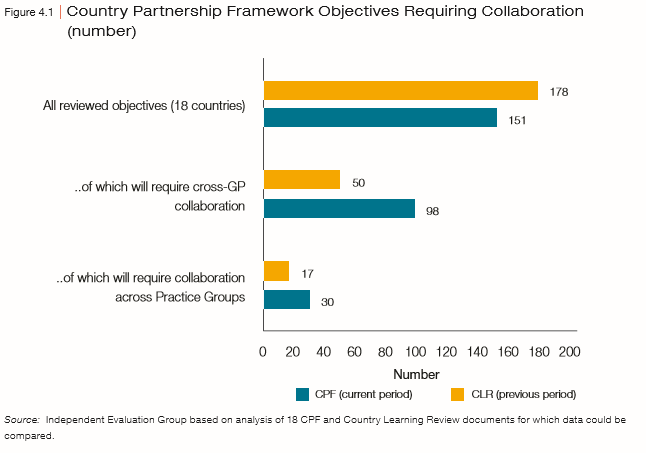
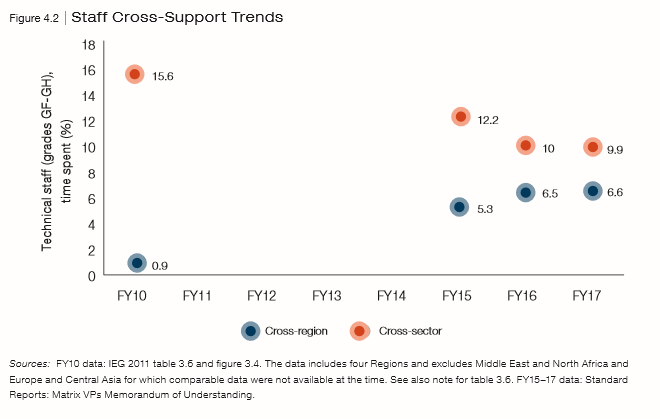
- There is demand for integrated solutions that draw on global knowledge. The World Bank can provide these solutions because of the leadership of Country Directors (CDs), who are supported by Program Leaders.
- Silos across Regions have decreased, as evidenced in increased interregional cross support.
- However, silos across Global Practices (GPs) have increased, and lending has become less multisectoral.
- The GPs’ incentives continue to favor own-managed lending, leading to competition and transaction costs.
- Mechanisms for working across GPs and between GPs and Country Management Units (CMUs) exist but are not always strong enough. Groups and roles tasked with integrating and arbitrating across boundaries sometimes lack the authority to do so.
Read more in Chapter 4: Collaboration for Integrated Solutions
View the structure of the World Bank operational complex as a result of the reforms to the operating model
See Glossary of Terms for more information about each staff position and technical groups
Recommendations
The main challenge going forward is to stimulate collaboration under the new operating model while enhancing the initial gains on knowledge flow. More robust mechanisms to work across the structure are needed while maintaining the global flow of staff and knowledge.
- Strengthen the approach to knowledge in the Global Practices (GPs) and Global Themes (GTs) with clear goals, roles, and mechanisms, budgets commensurate with mandates, and metrics for knowledge uptake, quality, and influence. This will entail improving incentives for knowledge production, curation, management, and sharing, whether performed by Global Leads and Global Solutions Groups or through other mechanisms. This could build on some of the good practices undertaken by some GPs.
- Improve budgeting systems to better incentivize knowledge flow and collaboration. This could be done, for example, through multiyear budgets or other mechanisms for enhanced year-on-year budget predictability; maintaining an adequate balance between budget allocations for Advisory Services and Analytics (ASA) and other knowledge functions and lending; addressing time lags between cross support and the related settlement by recipient budget units; exploring additional options for stronger budget incentives for collaboration; and continuing reforms of Bank–executed trust funds to improve their alignment with World Bank priorities.
- Better link the Global Practices and Regions to improve coordination and enhance responsiveness to clients. This could be done by enhancing the Region-facing responsibilities of GPs, providing Region-facing Practice Group Directors with adequate authority to arbitrate and link the two sides of the matrix; and, depending on the exact arrangement, by adjusting reporting arrangements for Practice Managers and Program Leaders.
- Ensure a stronger and more consistent use and role of the Program Leaders (PLs) as a mechanism for cross-sectoral collaboration, integrated solutions, and complex client dialogue. This could be done, for example, by clarifying expectations on PLs’ role, authority, and accountability; achieving a better balance between technical and connector roles; ensuring more effective dual reporting to CMUs and GPs; and continuing to recruit PLs based on both leadership skills and technical proficiency.
- Review the existing quality assurance arrangements to improve the quality of knowledge embedded in advisory and financing services. The review should identify ways to enhance the contestability of quality assurance mechanisms across GPs, covering quality at entry for lending and ASAs, implementation, and reporting at completion. It should also assess the balance of oversight responsibilities between GPs and CMUs.
- Ensure there is ongoing monitoring of the operating model and more continuity in change management efforts to enhance the organization’s ability to attain its knowledge flow and collaboration goals. This could be achieved by continuously collecting and reviewing data on organizational effectiveness and learn from past reforms and from other organizations.
Management should use this data to help it recognize and scale up successful innovations, and to design additional course corrections, as needed.
See Chapter 5: Conclusions and Recommendations
View the structure of the World Bank operational complex as a result of the reforms to the operating mode
See Glossary of Terms for more information about each staff position and technical groups







