Four Questions that Guided the Evaluation
This evaluation poses the question of the effectiveness of the Bank Group’s attempt at mainstreaming citizen engagement. More specifically, four lines of inquiry guided the evaluation:
1. What is the magnitude and nature of citizen engagement mainstreaming within World Bank Group operations, and how have they changed over time?
3. What are the extent and quality of monitoring and evaluation of citizen engagement activities, and what is the evidence of results (contribution to strengthening existing country systems for participation and to improved development outcomes)?
4. To what extent is the Bank Group corporate environment enabling citizen engagement mainstreaming?
As the World Bank Group Strategic Framework states, engaging citizens can be transformational and contribute to development outcomes. For this to happen, engagement needs to be “thick” and strategic, that is, use multiple and innovative tools to improve the country’s authorizing environment; it needs to ensure inclusion, so that diverse voices are heard, especially those of traditionally marginalized groups; it needs to build citizens’ and governments’ capacity to engage so that change can be long-lasting; and, crucially, it needs to be regular and continuous throughout the project cycle to ensure that citizen feedback is properly taken into account. So, how is the Bank Group doing?
Key Findings
The evaluation found that the World Bank Group succeeded in generating awareness and buy-in of the citizen engagement agenda among senior management and staff. Staff and management agree that citizen engagement is a responsibility of the Bank Group and a useful strategy to strengthen accountability in service delivery, mitigate risks, and anticipate problems. This change in mind-set, whereby the value of engaging citizens is now encouraged across the World Bank Group’s work, is a major achievement.

- The number of World Bank projects with non-safeguards-related citizen engagement mechanisms and citizen engagement indicators increased over the past few years. Based on a portfolio of 299 randomly selected World Bank investment projects, the percentage of projects with non-safeguards-related citizen engagement mechanisms has increased from 67 percent to 76 percent between FY11–13 and FY14–16, likely due to the increased buy-in of the mandate. Currently, more than 90 percent of investment projects approved during FY14–16 plan to use at least one citizen engagement mechanism (including mechanisms mandated by safeguards), that is, have a citizen-oriented design. The share of projects with at least one indicator in their results framework increased from 42 percent in FY11-13 to 63 percent in FY14-16, with a steady annual increase up to 95 percent in FY16.
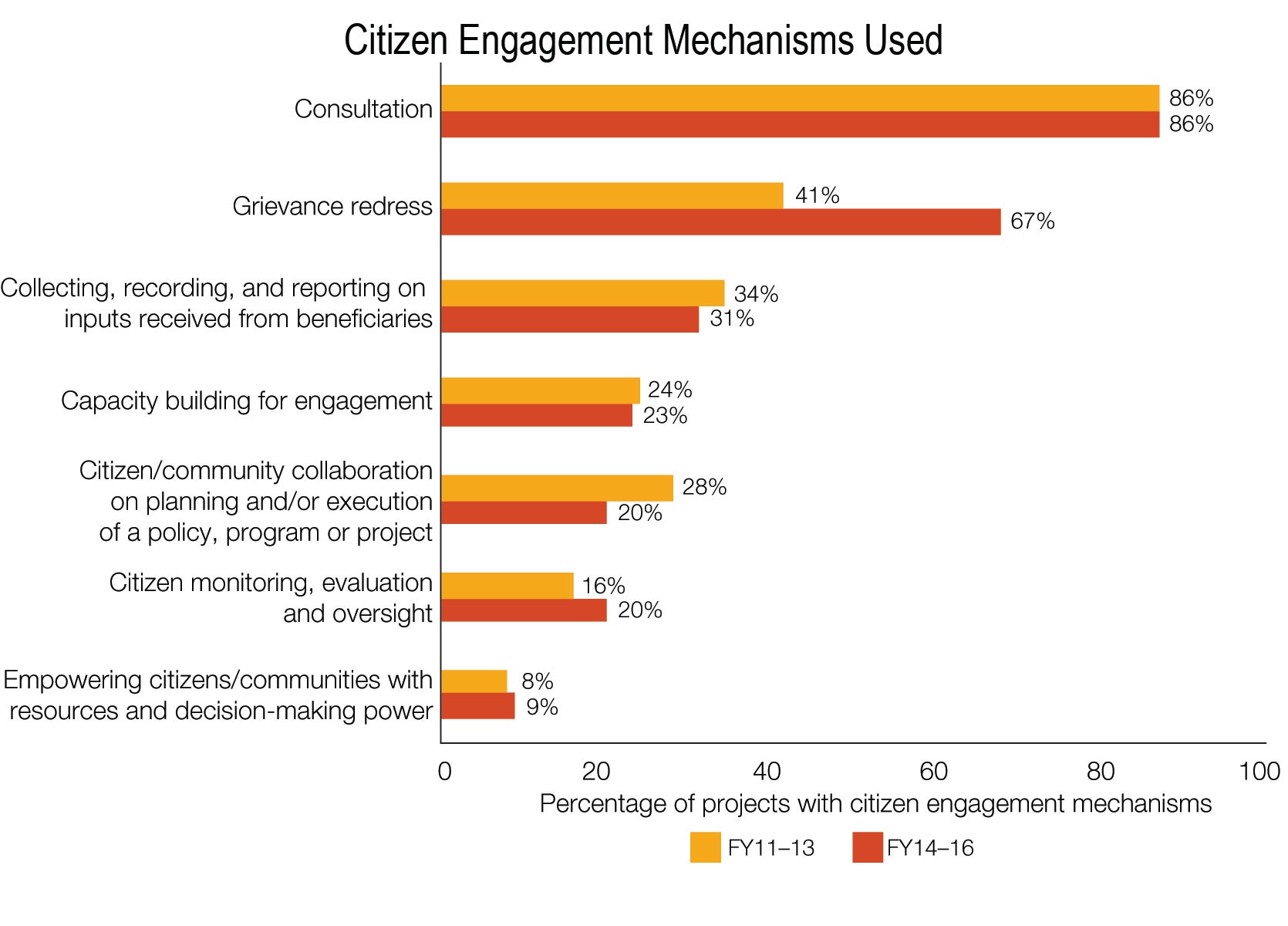
- Projects that resort to multiple mechanisms and pay closer attention to inclusion, albeit still a minority, are on the rise. Case studies conducted for this evaluation confirm the literature finding that “thick” approaches—those combining multiple tools to enable collective action and public sector responsiveness—are more promising than “thin” approaches—those that are not matched with vertical integration of independent monitoring and oversight or do not include support to increase government’s capacity to respond. In the World Bank’s portfolio, the share of projects with thick engagement has increased from 27 percent in FY11–13 to 38 percent in FY14–16 and even more markedly in the latest year, but it remains low.
- The share of projects that include beneficiary feedback indicators in their results frameworks has also increased markedly since the introduction of the corporate commitment. The empirical literature, echoed by this evaluation’s case studies, provides robust evidence that giving a tangible response to citizen feedback is fundamental to producing results, sustaining participation, and improving trust. Before the corporate commitment, 42 percent of projects had at least one indicator measuring how citizen feedback was provided; after the introduction of the commitment, this percentage increased to 63 percent in FY14–16, with a steady annual increase up to 95 percent in FY16.

- The International Finance Corporation leveraged Performance Standard 1 to encourage its clients to engage more systematically with stakeholders throughout their business cycle. Three positive patterns emerge. First, IFC clients more frequently plan to engage strategically with communities—via a range of mechanisms. Second, the mix of planned activities changed to include more proactive activities rather than reactive and risk-mitigation ones, such as GRMs, throughout the project cycle. Third, after the 2012 update IFC has more systematically promoted forms of stakeholder engagement directly related to clients’ business and the project activities and clients have progressively moved away from corporate social responsibility as the only form of engagement.
- The Bank Group has started to leverage the new country engagement model adopted in 2014 to consult with a wider range of stakeholders during the preparation of Country Partnership Frameworks (CPFs). Almost all CPFs approved between FY15 and FY17 refer to having consulted with civil society and, increasingly, with the private sector. Indigenous groups, youth, and women groups were specifically referenced in 43 percent of the documents and consultations with local governments and local NGOs in 63 percent of the CPFs reviewed.
- Development Policy Financing generally comply with the Operational Policy requirement of conducting stakeholder consultations. Almost all DPF operations approved between FY11 and FY16 found that almost all included some reporting on the consultation and participation of stakeholders.
- The corporate arrangements in place to oversee and coordinate the commitment (Citizen Engagement Secretariat and focal points) have worked well, operationalizing definitions to screen activities and projects. The regional citizen engagement focal points have been effective in providing expertise and support to operational teams, despite limited time and resources. The sectoral focal points have not been as effective; in general, Global Practices have been less active than the Regions in providing guidance and gathering knowledge of what works
The evaluation also found that, as the number of projects with a citizen-oriented design and citizen engagement indicators in results frameworks has increased, the application of quality standards in the design, implementation, and monitoring of citizen engagement, which is critical to achieve development results, has been limited.
- Projects that establish a “thick” citizen engagement (which is regular and continuous, uses multiple tools, and is embedded in country systems) are not the norm. Mechanisms implying a light degree of engagement (“informing” and “consulting”) are much more frequent than more intense forms of engagement (“collaborating” and “empowering”). Except in governance, social development projects, and formal CDD, the World Bank still favors “thin” approaches using only one or two mechanisms, which are short-lived and focus exclusively on gathering citizen feedback. Sixty-eight percent of the investment projects with citizen-oriented design in the evaluation sample (FY11–16) have thin engagement. The evaluation found that establishing thick engagement requires intensifying training, ensuring that adequate expertise is mobilized, improving synergies with other programs (such as the Global Partnership for Social Accountability), and strengthening knowledge management.
- Crucially, closing the feedback loop with citizens is not properly mainstreamed nor monitored. Most (70 percent) of the citizen engagement mechanisms reviewed describe at design how they plan to take citizen feedback into account. However, almost none signal whether they plan to inform citizens about the actions taken in response to their feedback. Details on the feedback received by those consulted during the preparation of country strategies is not commonly included in CPF documents, despite being essential to understanding how the feedback loop was closed. Only 20 CPFs (43 percent) reported the CSOs’ feedback on the themes of consultations and their proposed areas of engagement. A dismal two CPFs clearly documented how the feedback received was integrated. As for DPF, 40 percent did not specify which stakeholders were consulted and only one-quarter of the program documents reviewed included some discussion of the outcome of the consultations.

- Indicators rarely track results, many mechanisms are not measured in results frameworks, and reporting is still insufficient. Only 57 percent of the projects approved in FY14–16 with engagement indicators in their results frameworks have reported on at least one of the citizen engagement indicators included in their results frameworks. Consultations and GRMs are the most common mechanisms but the least measured ones. Most indicators are process or output oriented, and reporting in self-evaluation is scarce.

- IFC reporting, in particular, provides poor information on implementation and results. Stakeholder engagement plans are absent in the majority of IFC projects approved between FY15 and FY17. In addition, IEG found that a fourth of projects provide too little information to even understand how the client engaged with the community. Reporting is slightly more complete in high-risk projects, although generally insufficient also in this case.
- The insufficient attention to quality principle and emphasis on tools rather than results risk undermining the Bank Group’s objective to mainstream citizen engagement to improve development outcomes. Several of the case studies conducted for the evaluation show examples of citizen engagement mechanisms leading to positive behavior and relationship change. However, there is little evidence that citizen feedback is used to strengthen operations by informing project design or triggering course correction during implementation. Promoting reforms that enable citizen engagement is rarely an objective of DPF; DPF prior actions and triggers are rarely used to support policy reforms that could foster citizen engagement.
- More focus on capacity building and learning is warranted. Citizen and state actors’ lack of capacity and willingness to engage represent major constraints to successful engagement per the literature and Bank Group staff. Creating capacity requires a long-term investment that, although not feasible in all projects, is essential to improving collective action and producing lasting change beyond the life of the project. Yet, less than a quarter of projects (23 percent) reviewed had at least one engagement mechanism that included capacity enhancement activities in their design. The Global Partnership for Social Accountability (GPSA) is one of the few channels that the World Bank has for building capacity, but its potential is still underexploited

- Better synergies with other relevant agendas, such as the new Environmental and Social Framework, could support more substantial work through pooling of resources, capacity, and experience.. The new ESF embeds several elements of the citizen engagement agenda as it calls for an early, open, meaningful, and continuous engagement with stakeholders, providing opportunities for stakeholders’ views to be considered in project design, implementation, and monitoring; requires grievance redress mechanisms in all projects; emphasizes the use of existing borrower frameworks, with the goal of building more sustainable institutions and increasing efficiency. By moving from a pure risk management perspective to a more proactive engagement with stakeholders, the ESF has the potential to absorb many of the quality elements essential for achieving results. Moreover, the ESF agenda is more endowed with staff and resources than the citizen engagement agenda, is in the process of being strengthened through new hiring and a massive capacity building effort and has clear enforcement mechanisms.
- At the organizational level, dedicated staff time to operationalize the approach beyond ensuring compliance with the corporate target is limited. Given the Bank Group’s ambitious objective of mainstreaming citizen engagement to enhance and sustain development outcomes, the overall amount of dedicated human, technical, and financial resources are not fit for purpose. Moving forward, the organization should consider carefully the tensions between ensuring “quality” engagement that can lead to development outcomes and a “universal” approach that may remain superficial for many activities.

Recommendations
The Bank Group has succeeded in making citizen engagement a top priority and creating awareness and buy-in. However, aspects related to quality are typically not given sufficient attention at the design and monitoring stages. To sustain and deepen the effectiveness of the Bank Group’s citizen engagement efforts, the evaluation proposes the following recommendations:
Recommendation 1. As it defines future corporate priorities for citizen engagement, the World Bank should reflect in those priorities the need to achieve greater depth and quality of the citizen engagement activities it supports. This will entail building on the progress achieved under the strategic framework to promote a more strategic approach that incorporates deeper citizen engagement where opportunities arise. These future corporate priorities will need to be clearly communicated to staff and stakeholders.
Recommendation 2. The World Bank should encourage and support efforts of its regional, country and Global Practices teams to establish, where appropriate, “thick” citizen engagement that is regular and continuous, uses multiple tools, and is embedded in country systems. This could be achieved by more systematically using existing channels of dialogue and stakeholder engagement (such as Systematic Country Diagnostics, CPFs, and DPFs) and applying tools (such as roadmaps and indexes) to plan, monitor, and assess results achieved at the various levels (Region, country management unit, Global Practice). This would entail better synergies between Bank operations and other programs that support citizen engagement, including GPSA-financed activities; mobilizing adequate expertise to support Bank teams; investing in training for staff and stakeholders; and improving knowledge management.
Recommendation 3. The World Bank should strengthen the monitoring of its citizen engagement activities by systematically adopting results framework indicators that are results oriented. This will entail tightening the alignment between the citizen engagement mechanisms used in projects and the indicators that measure their quality and results, with special emphasis on indicators that show how feedback loops were closed and how diverse groups of stakeholders were included.
Recommendation 4. The World Bank should seize the opportunity of the implementation of the ESF to leverage citizen engagement mechanisms—beyond consultations and GRMs—to reach the objectives of managing social risks, strengthening country systems, and promoting social inclusion. This will entail better drawing on the existing expertise on citizen engagement and making citizen engagement more prominent in the ESF trainings, both for staff and for project implementation units.
Recommendation 5. IFC should ensure that its clients’ stakeholder engagement activities required by PS 1 in projects with affected communities are carried out during appraisal and supervision of the projects and systematically documented. This will entail mobilization of adequate expertise to systematically support clients and reporting that is comprehensive and results focused.
See Also:
IEG's launch event/live discussion Engaging Citizens for Better Development Results
BBL discussion, Citizen Engagement in MENA: Results & Potential Entry Point for Change, featuring IEG's Elena Bardasi









